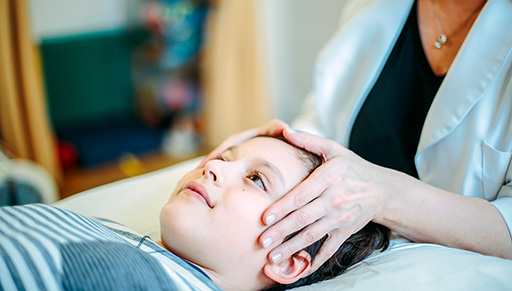
Osteopathic treatment using the cranial approach is very gentle, safe and effective in the treatment of babies and children.
Our Treatments
Osteopathy for Children




OSTEOPATHY FOR CHILDREN
Cranial osteopathic treatment is a very gentle, non-manipulative safe approach that it is often used when treating new born infants and young children. Gentle touch is applied to the baby’s head and body, enabling the inherent ability of the body to release stresses and balance itself 16,17.
Osteopathy is based on a principle that structure and function of the body are intimately related. This means that if the structure is not well balanced it may possibly affect the function of related areas. This principal is applied when the osteopath is accessing and treating new born infants and young children.
The osteopath will take a thorough case history enabling he or she to access the contributing factors to the baby or young child’s symptoms including: environmental factors and the family’s health history.
After the case history is taken and the assessment is done the osteopath may recommend cranial osteopathic treatment which may help restore balance to the baby or young child’s body.
Please note that the research references below are pilot studies. There is a need for larger trials to confirm
16Osteopathic manipulative treatment for the treatment of hospitalized premature infants with nipple feeding dysfunction. Lund GC, Edwards G, Medlin B, Keller D, Beck B, Carreiro JE. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2011 Jan;111(1):44-8.
17The use of cranial osteopathy in the treatment of infants with breast feeding problems or sucking dysfunction. Wescott N.Australian Journal of Holistic Nursing 2004 Apr;11(1):25-32. Review.
There have been pilot studies done on this subject, however more controlled studies have yet to be carried out to understand the full effects of cranial treatment on children.



More Research Papers
Nutritional supplements and other complementary medicines for infantile colic: asystematic review. Perry R, Hunt K, Ernst E. Pediatrics. 2011 Apr;127(4):720-33.
A preliminary assessment of the impact of cranial osteopathy for the relief of infantile colic. Hayden C, Mullinger B. 2006 May;12(2):83-90. Epub 2006 Feb 8.
Infantile colic: A critical appraisal of the literature from an osteopathic perspective. Kok Weng Lim. International Journal of Osteopathic Medicine 2006; 9:94-102.
Effect of different labor forces on fetal skull molding. Pu F, Xu L, Li D, Li S, Sun L, Wang L, Fan Y. Med Eng Phys. 2011 Jun;33(5):620-5.
Fetal head molding. Diagnosis by ultrasound and a review of the literature. Carlan SJ, Wyble L, Lense J, Mastrogiannis DS, Parsons MT. J Perinatol. 1991 Jun;11(2):105-11. Review.
Some important factors in the molding of the fetal head during vaginal delivery–a photographic study. Sorbe B, Dahlgren S. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1983 Jun;21(3):205-12.
Sagittal suture overlap in cephalopelvic disproportion: blinded and non-participant assessment. Buchmann EJ, Libhaber E.Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2008;87(7):731-7.
Osteopathy may decrease obstructive apnea in infants: a pilot study. Vandenplas Y, Denayer E, Vandenbossche T, Vermet L, Hauser B, Deschepper J, Engelen A. Osteopathic Medicine and Primary Care 2008 Jul 19;2:8.
A randomized controlled trial of the effectiveness of osteopathy-based manual physical therapy in treating pediatric dysfunctional voiding. Nemett DR, Fivush BA, Mathews R, Camirand N, Eldridge MA, Finney K, Gerson AC.Journal of Pediatric Urology 2008 Apr;4(2):100-6. Epub 2008 Jan 11
Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with osteopathy: results of a randomized controlled pilot study. Hundscheid HW, Pepels MJ, Engels LG, Loffeld RJ. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2007 Sep;22(9):1394-8.
Palpatory diagnosis of plagiocephaly. Sergueef N, Nelson KE, Glonek T. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice 2006 May;12(2):101-10. Epub 2006 Mar 29.
Effect of osteopathic manipulative treatment on gastrointestinal function and length of stay of preterm infants: an exploratory study. Pizzolorusso G, Turi P, Barlafante G, Cerritelli F, Renzetti C, Cozzolino V, D’Orazio M, Fusilli P, Carinci F, D’Incecco C.Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2011 Jun 28;19(1):15.
Osteopathic manipulative treatment and pain in preterms: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. CERRITELLI, F., CICCHITTI, L., MARTELLI, M., BARLAFANTE, G., RENZETTI, C., PIZZOLORUSSO, G., LUPACCHINI, M., D’ORAZIO, M., MARINELLI, B. & COZZOLINO, V. 2015. Osteopathic manipulative treatment and pain in preterms: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials, 16, 84.
General Movements in preterm infants undergoing craniosacral therapy: a randomised controlled pilot-trial. Raith, Wolfgang, et al. BMC complementary and alternative medicine16.1 (2016): 1.
IBC Care offers general osteopathy, visceral osteopathy, osteopathic care for pregnant women & children as well as Naturopathic Treatment - Functional Medicine Approach.
CHECK OUR FULL SERVICE LIST
- Hours and ServicesWhen you can book an appointment
Pre-treatment online consultation (compulsory prior to the first Face-to-Face consultation) – Monday & Wednesday: 2pm – 6pm
Face-to-Face consultation – Tuesday & Thursday: 10am – 6pm | Wednesday: 2pm – 6pm
- Book OnlineHow to make a booking
Booking an Appointment is a simple process. Please follow these instructions for online bookings.
- Contact usHow you can contact us
Please ring our friendly reception team on 020 7792 4499 or follow the link for the online booking.
- How to find IBC CareSee the map
IBC care is located at 9 Upper Wimpole Street, London, W1G 6LJ. View more for directions.
TESTIMONIALS
Words from our patients
trust her judgement and value her expertise.